Translate this page into:
Mycophenolate-Induced Dysphagia in a Kidney Transplant Recipient
Corresponding author: Kalathil K Sureshkumar, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Medicine Institute, Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA, United States. E-mail: kalathil.sureshkumar@ahn.org
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Sureshkumar KK, Ryhal R, Nashar K, Daloul R. Mycophenolate-Induced Dysphagia in a Kidney Transplant Recipient. Indian J Nephrol. doi: 10.25259/IJN_680_2024
Dear Editor,
Upper gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms such as dysphagia and odynophagia in immunocompromised hosts are generally caused by viral or fungal infections.1 We present a kidney transplant recipient who developed progressive dysphagia and odynophagia caused by mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) that improved after discontinuation of MMF and serial endoscopic esophageal dilatation.
A 49-year-old male [cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin G negative (CMV IgG −ve), Epstein-Barr virus immunoglobulin G positive (EBV IgG +ve)] underwent living donor kidney transplantation from his sister (CMV IgG +ve, EBV IgG +ve) using Thymoglobulin induction and tacrolimus/MMF maintenance along with infection prophylaxis using valgancyclovir, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and nystatin. Discharge serum creatinine was 1.5 mg/dL. One month later, he developed progressive dysphagia, odynophagia, reduced appetite, and weight loss. MMF was replaced with azathioprine. The upper endoscopy showed a benign intrinsic severe distal esophageal stricture that was dilated to 7 mm and biopsy showed focal acute inflammation [Figure 1]. Specimen stained negative for fungal elements, CMV and herpes simplex virus (HSV). He required nine more stricture dilatations in over three months to a final diameter of 18 mm. Dysphagia gradually resolved with better dietary intake and weight gain over the next few months.
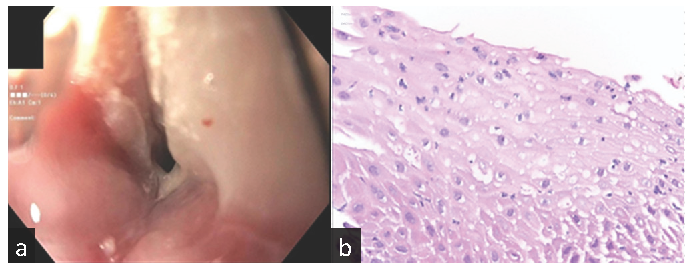
- (a) Upper endoscopy showing benign intrinsic severe distal esophageal stricture, (b) Stricture biopsy showing focal acute inflammation. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain x400.
MMF selectively acts on B and T lymphocytes. Gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity is reported in 40–85% of patients taking MMF and more commonly involves the lower GI tract.2 Upper GI toxicity usually results in ulcerative esophagitis, reactive gastropathy, and duodenal ulcers. MMF-related esophageal stricture is extremely rare. The mechanism of MMF-related GI toxicity is not clear but may involve MMF-induced blockade of guanosine nucleotide synthesis upon which the rapidly replicating enterocytes partially depend on, thus disrupting the GI epithelial barrier.3 MMF metabolites, including mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide, can elicit hypersensitivity and autoimmune reactions.4
MMF should be considered as a potential etiology for dysphagia from the esophageal stricture in a transplant recipient, especially when common etiologies such as reflux esophagitis and infectious esophagitis are excluded. A high index of suspicion is needed for early diagnosis and timely discontinuation of MMF, since a delay in the diagnosis can contribute to significant morbidity.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gastrointestinal complications of transplant immunosuppression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:277-87.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noninfectious gastrointestinal (GI) complications of mycophenolic acid therapy: A consequence of local GI toxicity? Transplant Proc. 2007;39:88-93.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycophenolic acid mediated disruption of the intestinal epithelial tight junctions. Exp Cell Res. 2014;322:277-89.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastrointestinal side effects of mycophenolic acid in renal transplant patients: A reappraisal. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:2440-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






