Translate this page into:
An Observational Study on the Clinicopathologic Features of Renal Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposition Disease
Corresponding author: Anila Abraham Kurien, Department of Pathology, Renopath Center for Renal and Urological Pathology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. E-mail: anila_abraham08@yahoo.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Malathi CV, Jansi Prema KS, Kurien AA. An Observational Study on the Clinicopathologic Features of Renal Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposition Disease. Indian J Nephrol. 2025;35:417-9. doi: 10.25259/IJN_708_2024
Dear Editor,
Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease (MIDD) is characterized by the deposition of monoclonal immunoglobulins in the glomerular and tubular basement membranes. Monoclonal immunoglobulins are paraproteins secreted by the clonal proliferation of an abnormal plasma or B cell lineage. Identification of the nature of the monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits using fluorescence microscopy helps classify MIDD into three types.1 Light chain deposition disease (LCDD) features a single light chain isotype (κ or λ). Heavy chain deposition disease (HCDD) shows a single heavy chain (γ, α, or µ). Light and heavy chain deposition disease (LHCDD) includes monoclonal light and heavy chains. MIDD can present with light chain cast nephropathy (LCCN).2 Our study presents an analysis of the clinicopathologic characteristics of monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease.
We reviewed the native kidney biopsies diagnosed with MIDD and MIDD+LCCN from August 2018 to May 2024. The glomeruli in the biopsies showed one of the following morphologies - nodular glomerulosclerosis, mild increase in mesangial matrix or normocellular. The clinicopathologic parameters were analyzed between MIDD and MIDD+LCCN groups as well as on the basis of glomerular morphology.
Out of 23,182 native kidney biopsies, 133 cases of MIDD (n=60, 0.25%) and MIDD+LCCN (n=70, 0.31%,) were identified. Ninety-four patients were males, and 87 presented with acute kidney injury (AKI). All patients had proteinuria, while 45.1% were in the nephrotic range. 52.6% of patients were hypertensive. The mean serum creatinine at presentation was 5.2±3.5 mg/dL. Seventy-one (53.3%) required dialysis at presentation. Serum electrophoresis showed a monoclonal M band in 22.5%. The pathologic spectrum included 41 patients with LCDD, 7 with HCDD, 12 with LHCDD, 69 with LCDD+LCCN, and 4 with LHCDD+LCCN [Figure 1].
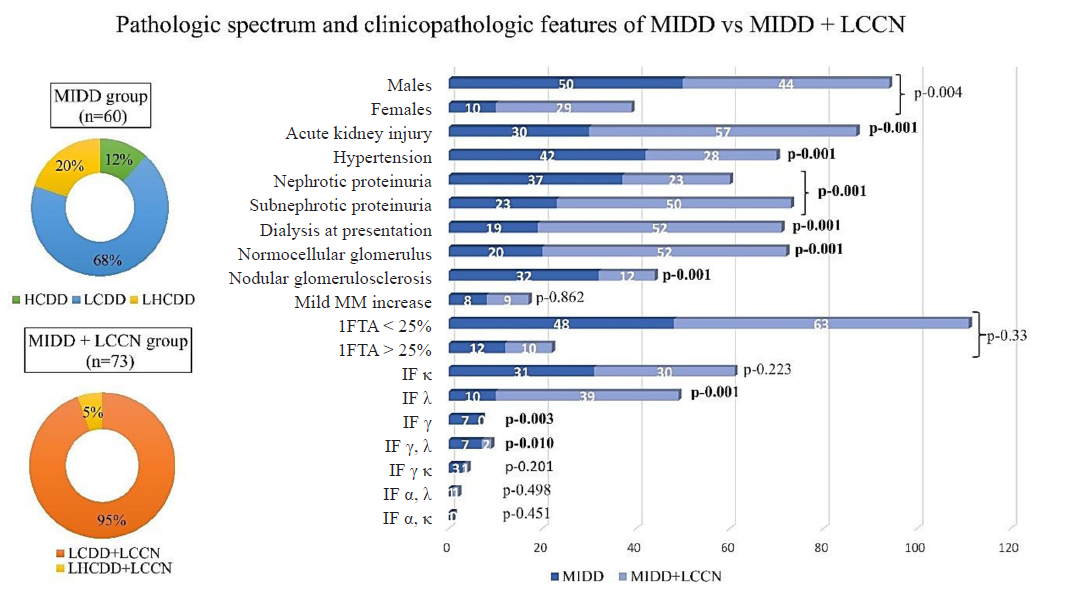
- Spectrum of pathologic diagnoses and clinicopathologic features in MIDD and MIDD+LCCN groups. MIDD: Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition diseases, LCCN: Light chain cast nephrology, HCDD: Heavy chain deposition disease, LCDD: Light chain deposition disease, LHCDD: Light and heavy chain deposition disease, MM: Mesangial matrix, IFTA: Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy, IF: Immunofluorescence, Significant p values are highlighted as bold values.
Glomerular morphology showed that 54.1% were normocellular, 12.7% had a mild mesangial matrix increase, and 33% had nodular glomerulosclerosis. Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) < 25% were observed in 83.4% of the cases. The tubules showed PAS-negative casts in the lumen, surrounded by inflammation and multinucleated giant cell reaction [Supplementary Figures 1 and 2] in those with MIDD + LCCN. Congo red staining was negative in all the cases.
Analysis of clinicopathologic features based on the glomerular morphology [Table 1] showed no difference in age or serum creatinine at presentation between the three groups. Patients with nodular mesangium presented with nephrotic proteinuria. Sub-nephrotic proteinuria and lower IFTA were observed significantly in cases with normocellular glomeruli [Table 1]. Immunofluorescence showed that isolated gamma positivity (HCDD cases) was associated with nodular mesangial expansion.
| Clinicopathologic features | Glomerular morphology | p value# | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normocellular | Nodular | Mild mm* increase | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Age (years) | 56.6 ± 11.9 | 52.4 ± 13 | 60.1 ± 10.1 | 0.052 |
| Gender | ||||
| Males | 51 (70.8%) | 36 (81.8%) | 7 (41.2%) | 0.041 |
| Females | 21 (29.2%) | 8 (18.2%) | 10 (58.8%) | |
| Acute kidney injury | ||||
| Yes | 50 (69.4%) | 24 (54.5%) | 13 (76.5%) | 0.155 |
| No | 22 (30.6%) | 20 (45.5%) | 4 (23.5%) | |
| Hypertension | ||||
| Yes | 27 (37.5%) | 37 (84.1%) | 6 (35.3%) | 0.001 |
| No | 45 (62.5%) | 7 (15.9%) | 11 (64.7%) | |
| Proteinuria | ||||
| Nephrotic | 24 (33.3%) | 30 (68.2%) | 6 (35.3%) | 0.001 |
| Sub nephrotic | 48 (66.7%) | 14 (31.8%) | 11 (64.7%) | |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 5.5 ± 3.5 | 4.9 ± 3.5 | 4.7 ± 3.6 | 0.588 |
| Immunofluorescence | ||||
| κ | 32 (44.4%) | 22 (50%) | 7 (41.2%) | 0.774 |
| λ | 33 (45.8%) | 9 (20.5%) | 7 (41.2%) | 0.032 |
| γ, λ | 4 (5.6%) | 3 (6.8%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0.323 |
| γ, κ | 2 (2.8%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0.749 |
| γ | 0 (0%) | 7 (15.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0.001 |
| α, λ | 0 (0%) | 2 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.128 |
| α, κ | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.652 |
| Interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy | ||||
| > 25% | 8 (11.1%) | 8 (18.2%) | 6 (35.3%) | 0.01 |
| ≤ 25% | 64 (88.9%) | 36 (81.8%) | 11 (64.7%) | |
| Dialysis at presentation | ||||
| Yes | 40 (55.6%) | 23 (52.3%) | 8 (47.1%) | 0.806 |
| No | 32 (44.4%) | 21 (47.7%) | 9 (52.9%) | |
*mm, mesangial matrix. #statistically significant p values are highlighted as bold
There was no difference between MIDD and MIDD+LCCN groups with respect to age, gender, or IFTA [Figure 1]. Patients with MIDD+LCCN presented more frequently with AKI, subnephrotic proteinuria, higher serum creatinine (p<0.001), and increased dialysis requirement than the MIDD group. Their biopsies showed predominant λ deposits and normocellular glomeruli.
Prior to the biopsy, 47 patients were diagnosed with multiple myelomas, and one was diagnosed with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Most of the patients received a bortezomib-based-chemotherapy regimen. Twenty-three patients succumbed during the treatment. On follow-up (n=33), 15 attained hematologic remission. Eighteen were on chemotherapy, of which four received autologous stem cell transplantation. Kidney parameters returned to normal in 23 patients. Eighteen patients were on maintenance hemodialysis. None underwent kidney transplantation.
Kidney biopsy was the first clue to diagnosing multiple myelomas in 14.6%-47.54% of the cases in Indian studies and 63.9% in our study.3,4 Immunofluorescence study using the panel of heavy and light chains (IgG, IgM, IgA, κ and λ light chains) in the biopsy tissue is essential to identify and classify MIDD.1,5
LCDD is a common subtype of MIDD. Substantial deposits of κ light and γ heavy chains are observed in LCDD and HCDD, respectively.6 Patients with LHCDD (7/12) in our study had predominantly γ and λ deposits. λ light chain restriction was common in the MIDD+LCCN group.
Nodular glomerulosclerosis is a characteristic pathologic feature of MIDD. MIDD can also present without mesangial sclerosis in the biopsy.7 Nephrotic proteinuria was noted in cases with nodular mesangium. λ deposition, sub nephrotic proteinuria, and lower IFTA (<25%) were associated with normocellular glomeruli. Nasr et al. documented the characteristics of 64 patients with renal MIDD.7 Light microscopy confirmed nodular sclerosis in 61% of their patients. Our study showed nodular glomerulopathy in 53.3% patients in the MIDD group.
The monoclonal light chains in MIDD can get filtered in the glomeruli, forming light chain casts. A few studies have compared the dual lesion of LCDD and LCCN and LCDD.2,6 Our study witnessed concurrence of LHCDD+LCCN, while LHCDD itself was less commonly reported in the literature.8
Lin et al. described that from clinical and pathologic perspectives, LCDD with cast nephropathy was distinct from MIDD cases.6 Similar to our study, they evidenced that concomitant cast nephropathy had higher serum creatinine and sub-nephrotic proteinuria.
Zand et al. included 87 patients comprising 45 with LCDD, 29 with myeloma cast nephropathy, and 13 with LCDD + cast nephropathy.2 Patients with LCDD had a higher degree of albuminuria than those with LCDD + cast nephropathy. Similar to our study, AKI and higher serum creatinine were observed in cases with LCDD + cast nephropathy than in those with just LCDD.
Our study had limited information on the laboratory parameters like free light chain assay, electrophoresis, and the follow-up of some patients.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Immunofluorescence staining for immunoglobulin heavy chain/light chain on kidney biopsies is a valuable ancillary technique for the diagnosis of monoclonal gammopathy-associated kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2021;100:155-70.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and prognostic differences among patients with light chain deposition disease, myeloma cast nephropathy and both. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56:3357-64.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Multiple facets of multiple myeloma in kidney biopsy: A multicenter retrospective study. Indian J Nephrol. 2024;34:31-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]
- Renal involvement in multiple myeloma: A 10-year study. Ren Fail. 2000;22:465-77.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standardized reporting of monoclonal immunoglobulin-associated renal diseases: Recommendations from a mayo clinic/renal pathology society working group. Kidney Int. 2020;98:310-313.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renal monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease: The disease spectrum. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:1482-92.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renal monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease: A report of 64 patients from a single institution. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7:231-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinicopathological characteristics of light and heavy chain deposition disease: A case series. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024;84:447-456.e1.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







