Translate this page into:
Potential Depression and Associated Factors Among Individuals Undergoing Dialysis: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Survey in Central Kerala
Address for correspondence: Dr. Jissa V. Thulaseedharan, Achutha Menon Centre for Health Science Studies, Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Trivandrum, Kerala - 695 011, India. E-mail: jissa@sctimst.ac.in
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
Depressive symptoms, along with invasive treatment modality, can impede the psychological wellness of the individuals and substantially affect their physical and social states and subsequently, the treatment outcome.[1] However, it is often not recognized. In this letter, we describe potential depression and the associated factors among individuals undergoing dialysis [Table 1].
| Characteristics | Total n=188 | Moderate to Severe depression | Odds Ratio (OR) and confidence interval (CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 143 | 23 | 16.1 | 1 | |
| Female | 45 | 15 | 33.3 | 2.42 | 1.09-5.33 |
| Education | |||||
| High school or above | 148 | 24 | 16.2 | 1 | |
| Seventh standard or below | 40 | 14 | 35.0 | 2.37 | 1.04-5.36 |
| Type of dialysis | |||||
| Peritoneal dialysis | 48 | 7 | 14.6 | 1 | |
| Hemodialysis | 140 | 31 | 22.1 | 1.67 | 0.66-4.20 |
| Age at diagnosis | |||||
| Up to 50 years | 108 | 17 | 15.7 | 1 | |
| Above 50 years | 80 | 21 | 26.3 | 1.71 | 0.80-3.61 |
We conducted a hospital-based cross-sectional survey involving 188 individuals undergoing dialysis (hemodialysis – 140 and peritoneal dialysis – 48) in four selected hospitals of Palakkad district, Kerala. We used the translated version of the nine-item depression module of the Patient Health Questionnaire–9 in Malayalam to evaluate depression.[23] The institutional ethics committee approved the study protocol before the conduct of the study. We used binary logistic regression analysis to estimate the odds ratios and 95% confidence interval for the associated factors of depression, where depression was categorized as 0 = “no/mild depression” and 1 = “moderate to severe depression.”
The age of participants ranged from 22 to 82 years, of which 60% were above 50 years. The proportion of male participants was 76%, and participants who had high school or above education was 79%. The proportion of individuals undergoing hemodialysis was 74%, and the age at diagnosis was less than 50 years old for 57%. Almost 52% of the participants were undergoing dialysis for more than 2 years. Among the total participants interviewed in this study, about 50% had no or minimal depression, followed by 29.3% with mild depression [Figure 1]. The prevalence of moderate to severe depression (n = 38) was 20% with a 95% confidence interval (CI) ranging from 14.7% to 26.7%.
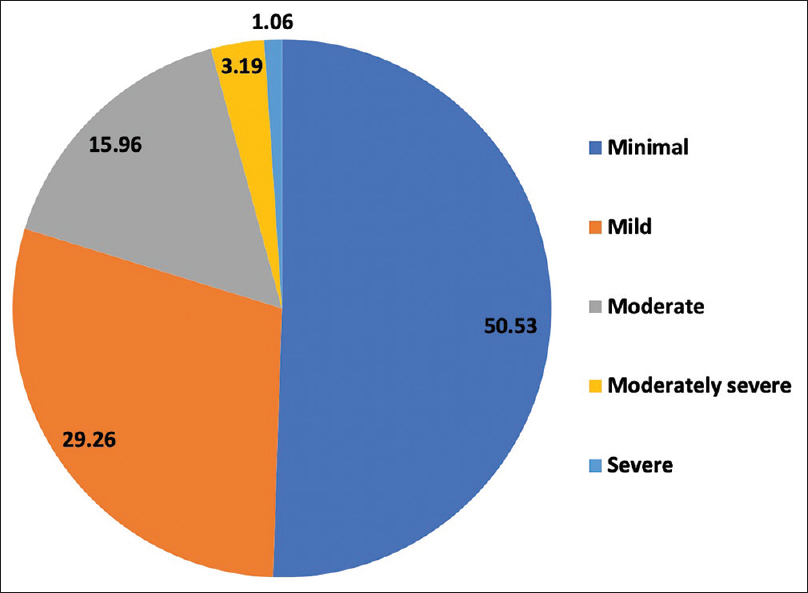
- Symptoms of depression among participants, assessment based on the score of Patient Health Questionnaire–9 scale
For the binary logistic regression analysis, we included the variables sex and education, which were significantly associated with depression in the bivariate analysis (P < 0.05), and the potentially relevant clinical variables such as type of dialysis and age at diagnosis. Although we observed an indication that moderate to severe depression symptoms were high among those with low socioeconomic status (SES), we did not include the variables for further analysis due to lack of significance. The results showed that females had 2.42 times higher odds of moderate to severe depressive symptoms compared with males (95% CI: 1.09–5.33). Individuals with low education had 2.37 times higher odds of moderate to severe depressive symptoms (95% CI: 1.04–5.36) compared with individuals with high school or above educational attainment. We found that individuals undergoing hemodialysis had 1.67 times higher odds of having moderate to severe depression compared with participants undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Similarly, the individuals diagnosed with the disease at above 50 years of age had 1.71 times more likely chance of presenting with moderate to severe depression compared with individuals diagnosed at the age of below 50 years. However, both these results were not statistically significant.
The more extended period spent with the dialysis machines in a week and frequent visits to the hospital along with stringent diet and fluid restrictions, consumption of too many medicines at a time, dependency on caregivers, economic burden, loss of freedom, and social loneliness affect the psychological well-being of individuals undergoing dialysis.[45] Along with that sociodemographic factors as well as clinical factors can gradually influence individuals undergoing dialysis to develop depressive symptoms. The recent Indian studies also suggest that gender, low SES, longer duration of dialysis, undergoing hemodialysis, and comorbid conditions are significant predictors of depression among chronic kidney disease patients.[678] The challenges faced by the women to fulfill their specific roles in families and the physical and economic dependency on other family members may make them more vulnerable to develop depressive symptoms. Peritoneal dialysis is more home-friendly and imposes fewer restrictions on the individuals; however, the role of caregiver is very much crucial as it needs consistent hygienic caring and supervision throughout the procedure.
Coming to the strengths and limitations of our study, we had to restrict our study to the four respective centers that offered permission to interview individuals undergoing dialysis. However, by including one government, two private, and one charitable trust, we could select patients from all types of facilities available in the district. We derived the sample size for the primary objective of estimating the prevalence of depression. This affects the study results with less power.
To conclude, observations from this study strongly suggest the need for routine assessment of depression in dialysis centers and to imply new interventions to improve the adapting skills for the individuals undergoing dialysis. Females and participants in lower education strata need more attention to make them adaptable to dialysis treatment. The holistic approach of physicians, staff nurses, social workers, and clinical psychologists can make a change in the psychological health of individuals undergoing dialysis. The introduction of new psychotherapeutic interventions along with the long-standing treatments can address the emotional needs and improve coping skills in individuals with chronic illness.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere thanks to the respective administrative officials and staffs in each hospital for their support in conducting the survey.
References
- Prevalence of anxiety and depression and its comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. J Bras Nefrol. 2014;36:325-31.
- [Google Scholar]
- The PHQ-9: Validity of brief description severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:606-13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Reliability and validity of PHQ-9 when administered by health workers for depression screening among women in primary care. Asian J Psychiatr. 2018;37:10-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Assessment of quality of life among end-stage renal disease patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Indian J Palliat Care. 2020;26:47-53.
- [Google Scholar]
- Depression and quality of life in patients on long term hemodialysis at a national hospital in Ghana: A cross-sectional study. Ghana Med J. 2018;52:22-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Depression and anxiety in patients of chronic kidney disease undergoing haemodialysis: A study from western Rajasthan. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020;9:4282-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prevalence of depression, anxiety and insomnia in chronic kidney disease patients and their co-relation with the demographic variables. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2017;38:35-44.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prevalence of depression and its associated factors among patients of chronic kidney disease in a public tertiary care hospital in India: A cross-sectional study. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:1165-73.
- [Google Scholar]






