Translate this page into:
Successful Renal Transplant in Castleman Disease - First Case Report from India
Address for correspondence: Dr. Sanjay Maitra, Flat No. 203, Uma Banjara, Road No. 13, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad - 500 034, Telangana, India. E-mail: drsanjaymaitra60@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Castleman disease (CD) comprises a rare group of heterogenous benign lymphoproliferative disorders with pathologic similarities. However, they present with diverse clinical manifestations. Renal involvement is rare in CD and is mainly reported with plasma cell type of multicentric disease. Various glomerular pathologies, interstitial involvement, or thrombotic microangiopathies have all been reported, some of which progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Progression of CD to ESRD is well documented; however, a patient on dialysis developing CD is rare. Moreover, kidney transplantations have seldom been performed on patients with CD. We report a patient with ESRD of unknown etiology who developed multicentric CD while on dialysis. He was treated with four doses of rituximab and later underwent a living kidney transplant with his wife as a donor. He has been clinically well ever since. We believe that this is possibly the first successful case of renal transplantation in CD with ESRD being reported from India.
Keywords
Castleman disease
end-stage renal disease on dialysis
renal transplant
Introduction
Castleman disease (CD) comprises a heterogeneous group of benign lymphoproliferative disorders, which share pathologic similarities; however, they present with diverse clinical manifestations. It is classified into two categories: unicentric CD (UCD) where a single lymph node or lymph node region is involved and multicentric CD (MCD) where multiple sites of lymphadenopathy exist. The latter is associated with systemic symptoms such as fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and recurrent pleural effusions unlike the former.[1] MCD is further subdivided into HHV-8-positive or HHV-8-negative patient groups. HHV-8-negative patients may exhibit features of POEMS (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, and skin changes) or TAFRO (thrombocytopenia, anasarca, fever, reticulin fibrosis and organomegaly) syndrome.[1] As per current estimates, the incidence of UCD and idiopathic multicentric disease are 15 and 5 per million patient-years, respectively.[2]
The association of kidney disease in CD is uncommon and so is ESRD needing dialysis.[34] Rarer still is a patient of ESRD later developing CD. There is only a single such case described; however, that patient had associated Kaposi’s sarcoma and did not undergo kidney transplantation.[5] Renal transplants in CD have rarely been reported and there are only a few case reports available.[6] We report a patient with ESRD who developed a plasma cell type of CD while on dialysis. He later underwent a living unrelated kidney transplant with his wife as the donor and had a stable post-transplant kidney function.
Case Report
A 50-year-old male patient with ESRD was admitted for a kidney transplant with his wife as a donor in January 2017. He developed fever 2 days before surgery. Repeated blood and urine cultures were negative as were the Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) profile and markers for vasculitis. His initial C Reactive Protein (CRP) was negative. Ultrasonogram (USG) showed bilateral contracted kidneys, no hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, or ascites; chest X-ray and whole-body PET-CT did not identify any focus of infection or malignancy. As he complained of severe back pain along with fever, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) spine was done that showed features of discitis for which a transpedicular disc biopsy was done. The culture from the disc biopsy grew Staphylococcus aureus, however it was negative for tuberculosis. His fever responded to intravenous (IV) flucloxacillin for 6 weeks and oral rifampicin 450 mg OD for 4 weeks.
He was re-evaluated for transplant in August 2017; however, computed tomography (CT) chest showed bilateral mild pleural effusion (left more than right), moderately enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, left axillary lymph nodes. and small bilateral supraclavicular lymph nodes [Figure 1]. Repeat PET-CT chest showed mediastinal lymph nodes with poor PET uptake, however, persistently high CRP and ESR and severe anemia was present.
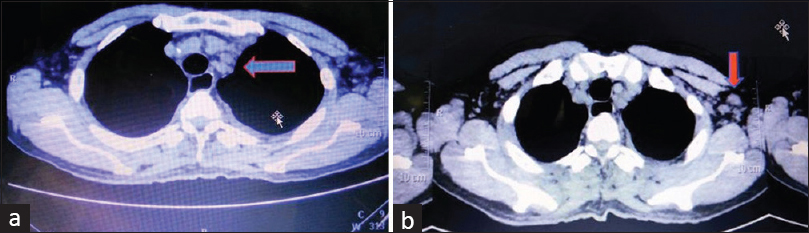
- Multiple enlarged discrete lymph node in (a) mediastinum and (b) left axilla
Axillary lymph node excision showed the vascular transformation of sinuses with no infection or malignancy. Excision biopsy of mediastinal lymph nodes done through video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery showed areas of suppuration; however, all cultures were negative. He was again prescribed IV antibiotics for 8 weeks, followed by oral antibiotics for 6 weeks. His left pleural effusion was found to be exudative, however it was negative for tuberculosis and malignancy.
In November 2017, he presented with persistent left exudative pleural effusion and was started on empirical anti-tubercular treatment (ATT) as per the pulmonologist’s advice. The pleural effusion persisted while he was on ATT till February 2018 when left pleurodesis was planned. Mediastinal biopsy samples sent for histopathology during surgery were suggestive of the plasma cell type of CD [Figure 2]. S.IL-6 levels sent after the diagnosis of CD were high, whereas HHV-8 was negative. He was started on weekly doses of rituximab for four doses as per the hematologist’s advice. He improved symptomatically and his pleural effusion volume rapidly decreased.
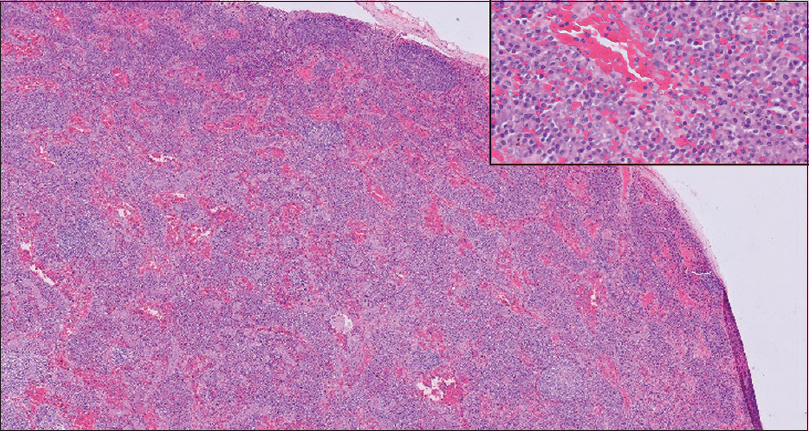
- Magnification 100×. Lymph node biopsy showing effaced architecture. Small follicles with concentric lymphocytes around it. Interfollicular infiltrate of plasma cells seen. (HE 100×) (Inset) High Power view of the same showing sheets of plasma cells in the interfollicular area. (HE 600×)
He was maintained on dialysis and after the necessary tests underwent a living kidney transplant with his wife as a donor on April 21, 2018. Induction was with thymoglobulin and steroids and maintenance immunosuppression was with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), and prednisolone. He is stable ever since in terms of clinical symptoms of recurrence of CD, graft function, and S.IL-6 levels. The important lab test results of the patient have been tabulated in Table 1.
| Parameters | Dates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan 2017 | Mar 2017 | Aug 2017 | Feb 2018 | Apr 2018 | Oct 2018 | Dec 2019 | Dec 2020 | June 2021 | ||
| Hb (g/dL) | 8.2 | 6.3 | 8.1 | 7.1 | TRANSPLANT APRIL 2018 | 10.4 | 13.8 | 14.2 | 15.7 | 14.6 |
| TLC (cells/mm3) | 5400 | 13820 | 6300 | 8400 | 19100 | 6500 | 10500 | 11200 | 10800 | |
| ESR (mm/h) | 92 | - | 100 | 84 | - | - | - | 10 | 15 | |
| S. CRP (mg/dL) | Neg | 156 | 172 | 191 | 17.4 | - | - | - | - | |
| S. Ferritin (ng/mL) | 396 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | - | - | - | 82.15 | - | 18.81 | 18.7 | 7.23 | 2.7 | |
| T. Protein (g/dL) | 6.1 | 8.0 | 6.7 | 7.2 | - | - | 6.9 | - | ||
| S. Albumin (g/dL) | 2.9 | 2.3 | 3.0 | 3.6 | - | - | 4.4 | - | ||
| S. Globulin (g/dL) | 3.2 | 5.7 | 3.7 | 3.6 | - | - | 2.5 | - | ||
| LDH (U/L) | 234 | 262 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| S. Creat. (mg/dL) | 6.4 | 5.6 | 8.6 | 6.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | |
| S. Tac (ng/mL) | - | - | - | - | 10.5 | 8.75 | 11.29 | 8.19 | 6.68 | |
Serum protein electrophoresis - No M Band, Bone marrow biopsy - Normal erythropoiesis, no abnormal cells detected. HHV-8, HIV, ANA negative
Discussion
The current diagnostic criteria for iMCD (idiopathic MCD) include two positive major criteria (histology and lymph node size) and two minor criteria (clinical features and investigations) while excluding the other differential diagnosis.[7] The distinctive lymph node histopathological features seen in CD are atrophic or hyperplastic germinal centers, prominent follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), hypervascularization, polyclonal lymphoproliferation, and/or polytypic plasmacytosis.[1] Pathologic evaluation with immunostaining is the main method of diagnosis. PET-CT or CT help stage the extent of disease and identify markers for follow-up. HIV needs to be excluded for HHV-8-associated diseases. Autoimmune disorders and lymphoma have to be excluded before proceeding to treat the condition.[1]
The association of kidney disease with CD is uncommon. Published data include a few case reports or small case series.[34] Histologically, mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis, membranoproliferative pattern of glomerular injury,[8] amyloidosis,[9] interstitial nephritis, and thrombotic microangiopathy have been reported in such cases.[10] To develop CD in a patient with ESRD on dialysis is extremely rare; only a single case is described in the literature in a patient with Kaposi’s sarcoma.[5] The plasma cell type of CD is most commonly associated with kidney disease, as is in our case.[3]
Diagnosis of iMCD in our patient was confirmed by lymph node biopsy and evidence of multiple lymphadenopathies and pleural effusion on CT scan. PET-CT scan on two separate occasions showed poor uptake of FDG-18 (SUV-Max values) possibly because of low disease activity.[11] Clinically, he had prolonged fever, lymphadenopathy, and recurrent pleural effusion. Investigations revealed anemia, raised ESR, S.CRP, and S.ferritin levels. Serum electrophoresis showed polyclonal hyperglobulinemia and M band was absent. HIV, HHV-8, ANA, P, and C-ANCA, anti-GBM antibodies were negative, consistent with the diagnosis of iMCD. IL-6 levels sent after the biopsy reports of CD were elevated.
The treatment options for patients with iMCD varies widely based on the physician’s preference. Being a rare disease, specific treatment recommendations are a few. Whereas mild disease responds to steroids or rituximab, siltuximab or tocilizumab is preferred in severe cases with high IL-6 levels. The single prospective randomized controlled trial with siltuximab shows reasonable efficacy and acceptable side effects of the drug. In patients with high VEGF levels, mammalian target of rapamycin (m-TOR) inhibitors such as sirolimus are preferred, whereas the other drugs tried have been combination chemotherapy, autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), bortezomib, thalidomide, and the IL-1-antagonist, Anakinra.[12]
Renal transplantation and CD rarely co-exist; there are two possible scenarios. The first is CD developing in patients after renal transplantation. An important differential would be post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD). A recent case series of six patients worldwide who developed CD after renal transplants had reported variable outcomes.[6] The second possibility is of patients of previously diagnosed CD undergoing renal transplantation. This is extremely rare and our patient falls in this category. Whereas some have reported successful outcomes, others have reported recurrence in the graft requiring treatment.[1314] Our patient has had a successful outcome till his last consultation. The only reported series of CD from India had no patients with renal involvement.[15] To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case from India where a patient of CD with associated ESRD underwent successful renal transplantation.
In India where tubercular pleural effusions are so common in ESRD patients, it is important to keep in mind other causes of exudative pleural effusion, which do not respond to ATT. CD could be one such rare cause and the physician should be aware of it.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Renal involvement in a large cohort of Chinese patients with Castleman disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(Suppl 3):119-25.
- [Google Scholar]
- The dialysed patient with both Castleman disease and Kaposi sarcoma. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998;13:2373-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Multicentric Castleman's disease in a renal allograft recipient:A case report and literature review. J Int Med Res. 2020;48:300060519897481.
- [Google Scholar]
- International, evidence-based consensus diagnostic criteria for HHV-8-negative/idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease. Blood. 2017;129:1646-57.
- [Google Scholar]
- Renal involvement in multicentric Castleman disease with glomeruloid hemangioma of skin and plasmacytoma. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:E17-24.
- [Google Scholar]
- End-stage renal failure from renal amyloidosis of the AA type associated with giant lymph node hyperplasia (Castleman's disease) Am J Nephrol. 1995;15:142-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Kidney involvement in multicentric Castleman disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:550-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- F-18 FDG PET/CT for the characterization of Castleman's disease according to clinical subtype. J Nucl Med. 20101614;51(Suppl 2)
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of idiopathic Castleman disease. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am. 2018;32:89-106.
- [Google Scholar]
- Successful renal transplantation for end-stage renal insufficiency developed in a patient with Castleman's disease. Transpl Int. 2013;26:e61-2.
- [Google Scholar]
- The efficacy and safety of anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal blockade in a renal transplant patient with Castleman disease:Early post-transplant outcome. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19:263.
- [Google Scholar]
- Presentation and outcome of Castleman's disease in immunocompetent hosts. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2016;32:468-74.
- [Google Scholar]







