Translate this page into:
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia in Hemodialysis Patients– The First Study from India
Address for correspondence: Dr. Jyoti Kotwal, Professor and Head, Department of Hematology, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Delhi - 110 060, India. E-mail: drjyotikotwal@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), a rare complication of heparin therapy, presents with thrombocytopenia. It leads to paradoxical thromboembolism and has high mortality if untreated. It is less recognized, especially in hemodialysis (HD) patients who are frequently exposed to heparin during dialysis because patients with renal failure may have many other causes of thrombocytopenia. We describe the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of five cases of confirmed HIT in hemodialysis (HD) patients at our center. The initial suspicion was made based on a high 4T score and positive gel card test followed by confirmation using the functional assay with heparin-induced platelet aggregation. These patients were treated according to the recent American Society of Hematology guidelines 2018 for HIT.
Keywords
Hemodialysis
heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
platelet aggregation test
Introduction
Heparin has been used ubiquitously in many medical and surgical fields and has fostered the development of cardiovascular surgeries, hemodialysis (HD), and extra-corporeal circuits. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a rare complication of heparin therapy, with overall incidence ranging from 5% to 10% in hospitalized patients.[1,2] The incidence in India is 5.6%.[3] In HD patients, the incidence is 0.6%–3.2%.[4,5] Thrombocytopenia and paradoxical thromboembolism are the characteristic features of HIT.[2] Patients with renal failure have many other causes of thrombocytopenia and platelet function defect;[6] thus, the diagnosis of HIT in these patient populations who are frequently exposed to heparin during HD is difficult. As HIT has high mortality rates of 20%–30%[2] and because of multiple causes of thrombocytopenia in patients with renal failure, a high index of suspicion is required to promptly diagnose HIT so that appropriate therapy can be given to prevent mortality and morbidity.
In the present study, we describe five cases of confirmed HIT in the setting of HD diagnosed over a period of 5 months from August 2021 to December 2021 in our hospital, a tertiary care center in North India and the only center doing the confirmatory functional assay for HIT in India. Initial suspicion of HIT was made based on the 4T score,[7] which includes thrombocytopenia, timing of thrombocytopenia, thrombosis, and ruling out other causes of thrombocytopenia [Table 1]. Low 4T scores (0–3) were found to have a high negative predictive value.[7] Further laboratory tests for HIT were done in patients having a 4T score of ≥4 as per the American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2018 guidelines[8] by both immune and functional assays. The objective is to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of HIT in HD patients so that early treatment can be initiated.
| 4Ts | Defining Events | Score=2 | Score=1 | Score=0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia | Fall in platelet count from baseline | >50% And |
30-50% And |
<30% Or <10,000/µL |
| Nadir platelet count | ≥20,000/µL And no surgery within the preceding 3 days |
10-19,000/µL Or Platelet count fall >50% from baseline but surgery within the preceding 3 days |
||
| Timing of platelet count fall | Onset of fall in platelet count from the start of heparin | 5-10 days or ≤1 day with prior heparin exposure within 30 days | Uncertain time course but likely 5-10 days or After day 10 or Within 1 day with prior heparin exposure in the past 31-100 days |
<4 days and no recent heparin exposure |
| Thrombosis (other clinical features) | -- | Confirmed new thrombosis Or Skin necrosis at the site of heparin injection Or Adrenal hemorrhage Or Acute systemic reaction to IV UFH |
Recurrent venous thromboembolism in a patient receiving therapeutic anticoagulation or Suspected thrombosis or Erythematous skin lesions at heparin injection sites |
None |
| Other causes for thrombocytopenia | -- | None obvious | Possible | Probable/definite |
Cases
Clinical details, investigations, and outcomes of patients are compiled in Table 2, and the first case is described in detail here.
| Case No | Age (in years) | Sex | Comorbidities | Evidence of infection | Baseline creatinine (mg/dL) | CBC on presentation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum procalcitonin (ng/mL) | Blood culture | Urine culture | ||||||||
| 1 | 59 | F | HTN, morbid obesity, type 2 DM, CKD 3 | 5.5 | Negative | Klebsiella pneumoniae | 5.4 | Hb-9.8 g/dL TLC-11600/μL Plt-160000/μL | ||
| 2 | 48 | F | Type 2 DM, HTN, hypothyroidism, CKD V on MHD | 1.95 | Negative | Negative | Hb-7.2 g/dL TLC-4820/μL Plt-213000/μL | |||
| 3 | 61 | F | type 2 DM, multiple hepatic cysts, AKI | 117.8 | Negative | Candida tropicalis | 7.13 | Hb-6.3 g/dL TLC-18730/μL Plt-271000/μL | ||
| 4 | 64 | F | HTN, OSA, post covid pulmonary hypertension, AKI on CKD | 0.57 | Negative | Negative | 5.75 | Hb-7.1 g/dL TLC-25960/μL Plt-61000/μL | ||
| 5 | 70 | M | HTN, hypothyroidism, right shoulder & wrist fracture post-surgery, CKD5 | 1.54 | Negative | Negative | 6.44 | Hb-7.8 g/dL TLC-21320/μL Plt-73000/μL | ||
| Case No | Day of onset of thrombocytopenia | Nadir platelet | Symptoms after onset of thrombocytopenia | 4T score | Antigenic (Gel card) for anti-HPF4 IgG antibodies | Heparin induced platelet aggregation test (PAT) | Therapy given | Outcome | ||
| 1 | D9 | 59000 | Nil | 4 | + | + | Heparin-free HD, Fondaparinux | Improved | ||
| 2 | D9 | 18000 | Per vaginal bleed | 5 | + | + | Heparin-free HD, Fondaparinux | Improved; discharged on rivaroxaban for 4 weeks. | ||
| 3 | D8 | 23000 | Pulmonary hemorrhage | 5 | + | + | Heparin-free HD, platelet transfusion; No anticoagulants due to pulmonary hemorrhage | Expired | ||
| 4 | D6 | 36000 | DVT, Skin necrosis at the heparin injection site | 6 | + | + | Heparin free HD, Fondaparinux, apixaban | Improved | ||
| 5 | D15 | 45000 | Thrombosis, erythematous rashes | 4 | + | + | Heparin free HD | Expired | ||
AKI-Acute kidney injury, CBC-Complete blood count, CKD-Chronic kidney disease, DM- diabetes mellitus, F-female, Hb-Hemoglobin, HD-hemodialysis, HTN-hypertension, M-male, OSA-Obstructive sleep apnea, Plt-Platelet, TLC-total leukocyte count
Case 1
A 59-year-old female, a known case of chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 3, was admitted with breathlessness, edema, oliguria, and fever. She had pallor and suprapubic tenderness. Investigations were consistent with urinary tract infection. She was treated with intravenous (IV) antibiotics and HD in which unfractionated heparin (UFH) was used. Platelets fell on the 9th day of dialysis with nadir 59000/μL on day 11. Her 4T score was 4. Antigenic (Gel card) test for anti-heparin-platelet factor-4 complex (anti-HPF4) IgG antibodies was positive [Figure 1]. Heparin-induced platelet aggregation test (PAT), which is one of the confirmatory functional assays for HIT[3,8] and looks at the activation of normal donor platelets by the patient’s serum in the presence of low-dose heparin, was positive [Figure 2], thus confirming the diagnosis of HIT. The patient was treated with fondaparinux and heparin-free HD. Her platelet count improved in 2 weeks, and she was discharged on fondaparinux for 2 more weeks as per the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) guidelines.[9]

- Gel card test for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia tested for anti-HPF4 IgG antibodies: number 1 shows positive control, number 2 shows negative control, and number 5 shows the positive test result of case 1. (Original figure)
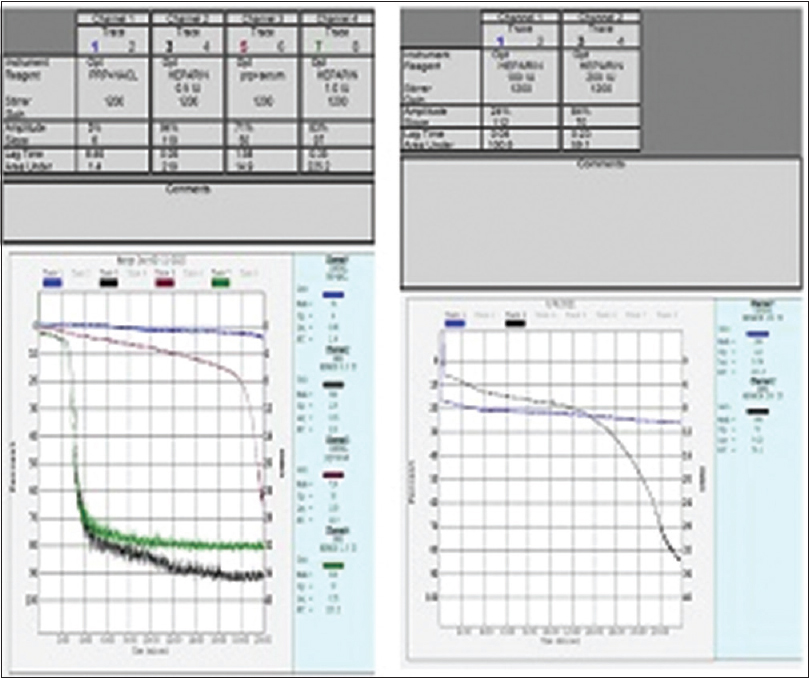
- Heparin-induced platelet aggregation test (PAT) of case 1 showing no aggregation with donor platelet-rich plasma (PRP) + saline, PRP + patient’s serum alone and with high dose heparin (100 IU and 200 IU). However, there is aggregation when the patient’s serum is added to PRP along with low-dose heparin (0.5 IU and 1.0 IU). (Original figure)
Among the five cases described in this series, there were two mortalities. The cause of mortality in case 3 was pulmonary hemorrhage due to the primary disease, double positive anti-GBM, and ANCA-associated vasculitis, whereas in case 5, the mortality was due to pulmonary embolism that was directly related to HIT.
Discussion
HIT is a prothrombotic disease caused by the development of antibodies against HPF4 complex. Various factors affect the incidence of HIT, such as the type of heparin used (LMWH causing 10-fold lesser HIT than UFH,[10] even lesser with fondaparinux), treatment settings (surgical more than medical[2] patients, probably due to massive amounts of PF4 released during surgeries), and investigations used for diagnosis. The incidence in dialysis patients was estimated to be 3.2% in patients newly undergoing dialysis[4] and 0.6% in patients on chronic dialysis,[5] but no data are available from India. We had five cases among 9579 sessions of HD in 790 patients, thus an incidence of 0.63% in our setting. Higher doses of heparin as in cardiopulmonary surgeries may increase the frequency of HIT antibodies but not clinical HIT.[2] However, HIT antibody production may be triggered with minimal heparin exposures as in IV catheter flushes.[11]
When heparin binds to the platelet surface, positively charged platelet factor-4 released from α granules of activated platelets binds negatively charged proteins on endothelium and anions such as heparin.[12] The binding of IgG antibodies to neoepitopes on HPF4 complexes cross-link Fcγ receptors on platelets and monocytes leads to their activation and thrombin generation.[12]
The most common presentation of HIT is thrombocytopenia, followed by thrombosis.[2] Platelets fall more than 50% from the baseline[2] between 5 and 10 days from heparin initiation, but sometimes before 5 days if there is prior heparin exposure within the past 3 months.[13] Venous thromboembolism is more common than arterial thrombosis.[2] Other manifestations are skin necrosis at heparin injection sites, acute systemic reactions to heparin bolus, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.[14]
Multiple scoring systems have been introduced to predict HIT; however, only 4T score [Table 1] has been validated.[7] A low 4T score can rule out HIT as it has a high NPV of 100%. However, intermediate (4–5) and high (6–8) scores are not diagnostic due to a low positive predictive value (PPV).[7] Laboratory tests for HIT include immunoassays and functional assays. Immunoassays (e.g., ELISA and Gel-card) detect anti-HPF4 antibodies and have a high sensitivity (85%) but low PPV.[3] Gel-card test is quicker, cost-effective, and can be done on a single sample, whereas ELISA is done in batches, thus requiring more samples and a high turn-around time.[3] The main limitation is the detection of non-pathogenic (IgM and IgA) antibodies. IgG-focused EIAs are more specific. HPF4 antibodies may be positive without clinical HIT.[2] Weakly positive immunoassays are less likely to be associated with clinical HIT.[13] Functional assays such as serotonin release assay and PAT have a high specificity (100%) in detecting platelet-activating anti-HPF4 antibodies but are available only in referral centers.[3]
The approach to HIT was recently revised in ASH 2018 guidelines[8] and is detailed in Figure 3. Treatment consists of discontinuing heparin products and starting a non-heparin anticoagulant, such as direct thrombin inhibitors (DTI), argatroban, and fondaparinux.[8] Warfarin should never be started in the acute phase as protein-C deficiency worsens the procoagulant state, causing gangrene.[15] Warfarin can be started after the platelet counts normalize. It is overlapped with DTI for at least 5 days after achieving the target INR; then, DTI is discontinued. The recommended duration of treatment in HIT without and with thrombosis is 4 and 12 weeks, respectively.[9] Platelet transfusion should be avoided unless there is uncontrolled bleeding.[8] Further re-exposure to heparin should be delayed by at least 3 months.
![Approach to diagnosis of HIT as per the ASH 2018 guidelines[8]](/content/170/2023/33/6/img/IJN-33-459-g003.png)
- Approach to diagnosis of HIT as per the ASH 2018 guidelines[8]
Conclusion
Untreated HIT can lead to high mortality and morbidity. As patients on hemodialysis are exposed to heparin frequently and their disease per se may cause mild thrombocytopenia, a high index of suspicion is required to diagnose and treat HIT promptly.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Heparin induced thrombocytopenia:Incidence and laboratory approach to diagnosis in Indians. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2014;57:31-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Heparin induced thrombocytopenia in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996;28:82-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Frequency of anti-heparin-PF4 complex antibodies (HIT antibodies) in uremic patients on chronic intermittent hemodialysis. Pathphysiol Haemost Thromb. 2006;35:445-50.
- [Google Scholar]
- Platelets in liver and renal disease. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016;2016:251-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prospective evaluation of the “4Ts”score and particle gel immunoassay specific to heparin/PF4 for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:1373-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism:Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2018;2:3360-92.
- [Google Scholar]
- Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients treated with low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1330-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment and prevention of heparin induced thrombocytopenia:Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th Ed:American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;114:495S-530S.
- [Google Scholar]
- Antibodies from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis are specific for platelet factor 4 complexed with heparin or bound to endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1994;93:81-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Laboratory diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Int J Lab Hematol.. 2019;41:15-25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Heparin-induced skin lesions and other unusual sequelae of the heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome:A nested cohort study. Chest. 2005;127:1857-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- Warfarin treatment of deep vein thrombosis complicating heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a risk factor for initiation of venous limb gangrene:Report of nine patients implicating the interacting procoagulant effects of two anticoagulant agents. Thromb Haemost. 1995;73:1110.
- [Google Scholar]







