Translate this page into:
Perinephric abscess with extension into mediastinum and epidural space
Address for correspondence: Dr. V. Sivakumar, Department of Nephrology, Sri Venkateswara Institute of Medical Sciences, Tirupati - 517 507, India. E-mail: sa_vskumar@yahoo.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Perinephric abscess is accumulation of pus in the space between the renal capsule and the Geroto's fascia. The pus that accumulates in the perinephric space, may extend in several directions. Extension into the the mediastinum and spinal epidural space is unusual. Such situation is presented in this report.
Keywords
Epidural space
extension
mediastinum
perinephric abscess
Introduction
Perinephric abscess is a collection of pus in the space between the kidney and Gerota's fascia. The abscess is usually confined to Gerota's fascia but may extend in several directions presenting as flank abscess, scrotal abscess, or subphrenic abscess. Rarely, it may perforate intraperitoneally or into the colon.[12] We did not find in our literature search the extension of perinephric abscess into the mediastinum and epidural space, hence is the interest in reporting this case. Patient recovered with appropriate management.
Case Report
A 52-year-old man, presented to casualty with a short history of fever, dysuria, and right loin pain for 10-days and swelling in the right inguinoscrotal region for 4-days. There was no pyuria or hematuria. On evaluation, he had a tender right lumbar and iliac mass extending into inguinoscrotal region with scrotal swelling, leukocytosis, severe renal failure, and metabolic acidosis. Blood and pus cultures grew Escherichia coli and appropriate antibiotics were given according to sensitivity pattern. He received hemodialysis for renal failure. Ultrasound of the abdomen revealed abscess in the right kidney with perinephric and psoas extensions and pyocele in right scrotum. Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen showed presence of renal abscess and perinephric collection with air, extension through anterior abdominal wall into the right scrotum. There was a pocket of collection with air in the epidural space of 12th thoracic vertebra [Figures 1 and 2]. CT chest showed pneumopericardium [Figure 3]. Surgical drainage was established in scrotum, anterior abdominal wall, and psoas regions. Patient recovered in two weeks and was discharged. No recurrence was observed in the followup.

- Non-contrast CT scan abdomen axial view showing biloculated collection of air with fluid (solid arrow) in the extraperitoneal location of anterior abdominal wall displacing the colon medially
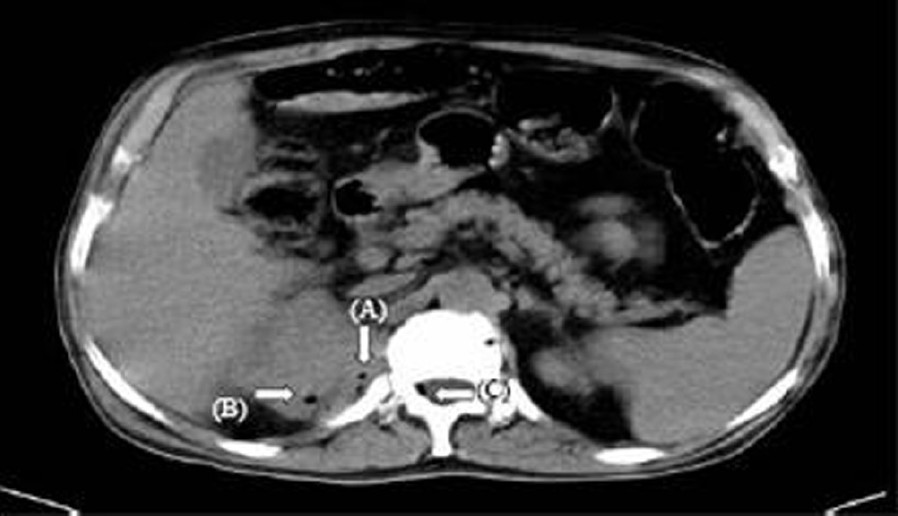
- Non-contrast CT abdomen axial view showing foci of air in the upper pole of the right kidney (solid arrow A), posterior pararenal space (solid arrow B), epidural space of 12th thoracic vertebra (solid arrow C)
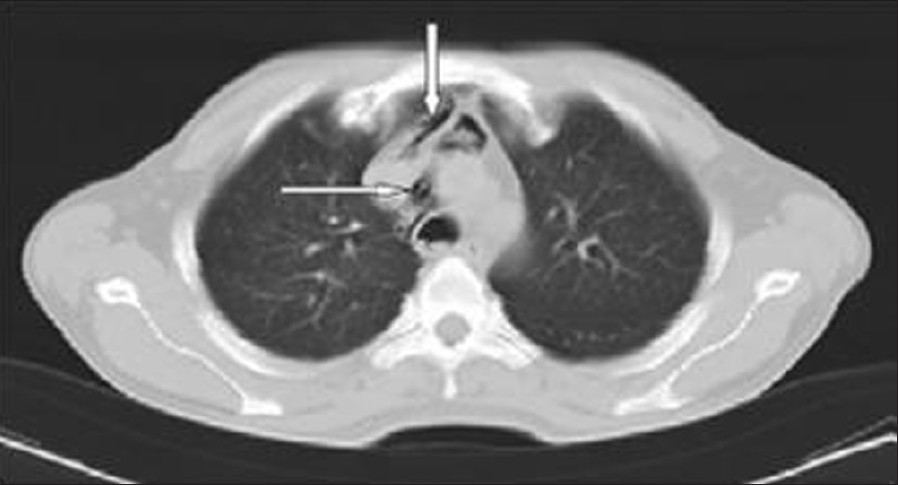
- Non-contrast CT scan of the chest axial image showing pneumomediastinum (solid arrows)
Discussion
Perinephric abscess is accumulation of pus in the space between renal capsule and Gerota's fascia. The Gerota's fascia is comprised of a thin anterior layer known as fascia of Toldt and thicker posterior layer known as fascia of Zuckerkandl. These layers fuse superiorly with the diaphragm and laterally with the transversalis fascia; medially, the anterior layer passes infront of the great vessels and is continuous with that of the contralateral side, while the posterior layer of Gerota's fascia fuses with the fascia covering psoas and quadratus lumborum muscles and the vertebral bodies. Inferiorly, the anterior and posterior leaves of Gerota's fascia fail to fuse and the perinephric fat is continuous with the pelvic fat. As pus accumulates in the perinephric space, it may extend in several directions. Downward extension may produce an abscess in the groin or paravesical area. The abscess may extend medially and penetrate into the peritoneum or laterally and perforate the colon. Superior extension may present as subphrenic abscess or penetrate the diaphragm resulting in empyema, lung abscess, or perinephrobronchial fistula.[2–4] In our patient, we found the extension of perinephric abscess into the psoas area, anterior abdominal wall, and right scrotum. In addition, the extension into mediastinum presenting as pneumomediastinum and extension into epidural space of 12th thoracic vertebra manifesting as an air pocket. We have also noticed extensive gas formation in the abscess regions. Our literature search did not show the reports of extension into the mediastinal and epidural spaces.
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.







